使用MkDocs和Github快速搭建网页文档库
以一个成功使用MkDocs与Github Actions以及Github Pages部署的课程资料库为例,直接介绍搭建流程,读者可根据需求对该流程进行更改,以搭建个性化的静态文档库
使用MkDocs和Github快速搭建网页文档库
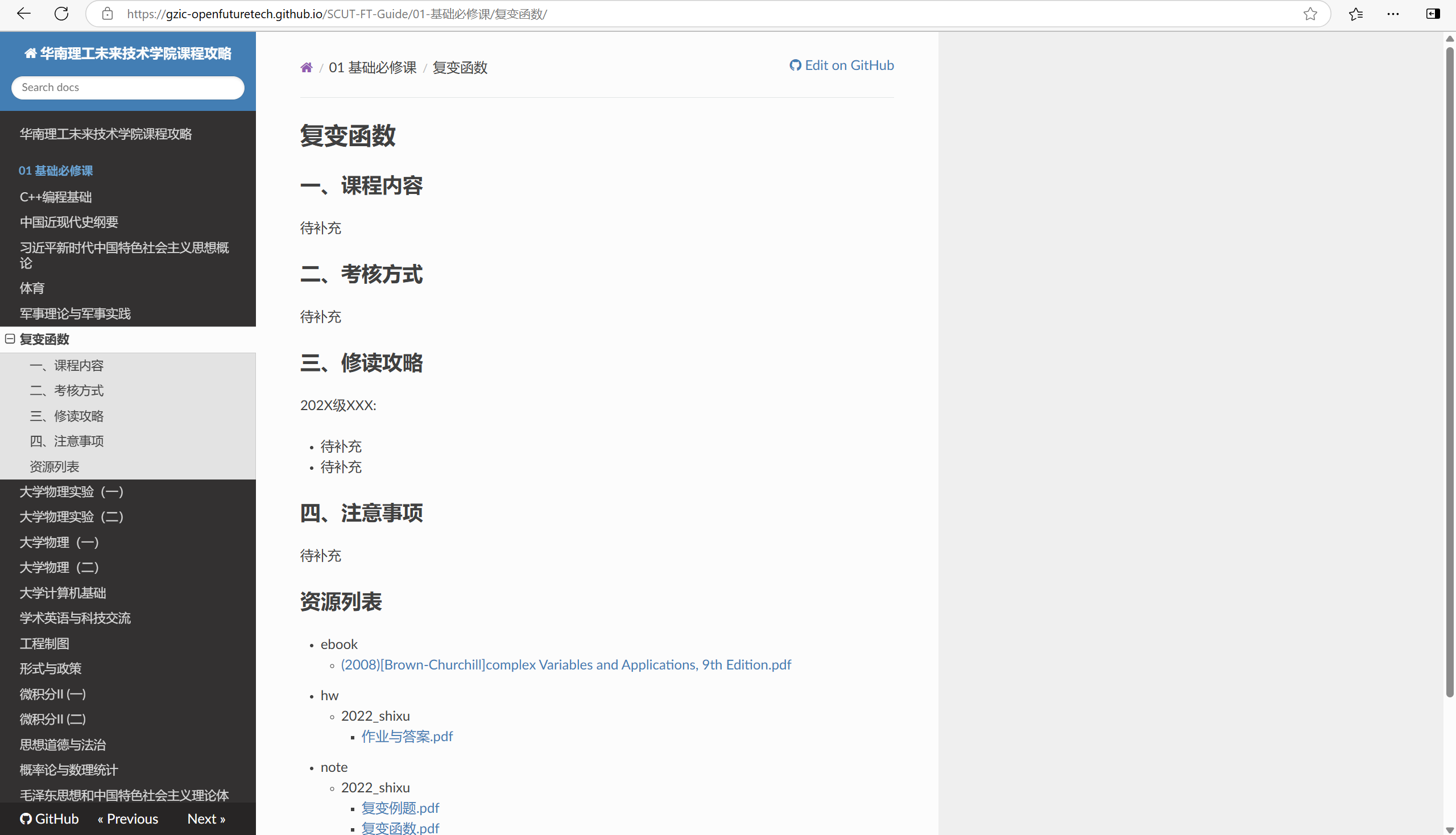
一、案例展示
- 本文以我搭建的华南理工未来技术学院课程攻略为例,其源码位于此仓库(难保证该仓库的配置在未来不会变化,此处严谨声明一下,行文时用的是仓库的该版本)
3.2 部署流程
3.2.1 创建MkDocs配置文件
1
2
3
site_name: 必填项,设置网站页面的标题
theme: 可选项,设置网页采用的主题样式,无此字段就采用默认样式
repo_url: 可选项,填了就会在生成的页面内提供链接到此地址的入口
3.2.2 编写目录生成脚本
- 有了
mkdocs.yml配置文件后,MkDocs还需要在根目录下有一个docs文件夹,其内至少要有一个index.html才可显示页面 - 若想在显示页面,需使用
Python环境下的mkdocs包才可以使用相应指令进行构建(若需在本地构建运行,参考官网指引,本文中不多赘述),在根目录新建requirements.txt,将该依赖项写入其中,以便后续在Github Actions的工作流中安装依赖
1
mkdocs
- 此时我们的根目录中包含上述新建的文件、以及我们欲发布的资源文件,目录如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
│ .gitattributes
│ .gitignore
│ LICENSE
│ mkdocs.yml
│ README.md
│ requirements.txt
│
├-.git
| ├-...
|
├─01-基础必修课
│ ├─C++编程基础
| ├-...
|
├─02-专业基础课
│ ├─3D视觉智能技术
| ├-...
|
├─03-选修课
│ ├─3D视觉智能技术
| ├-...
|
└─04-通识选修课
├-...
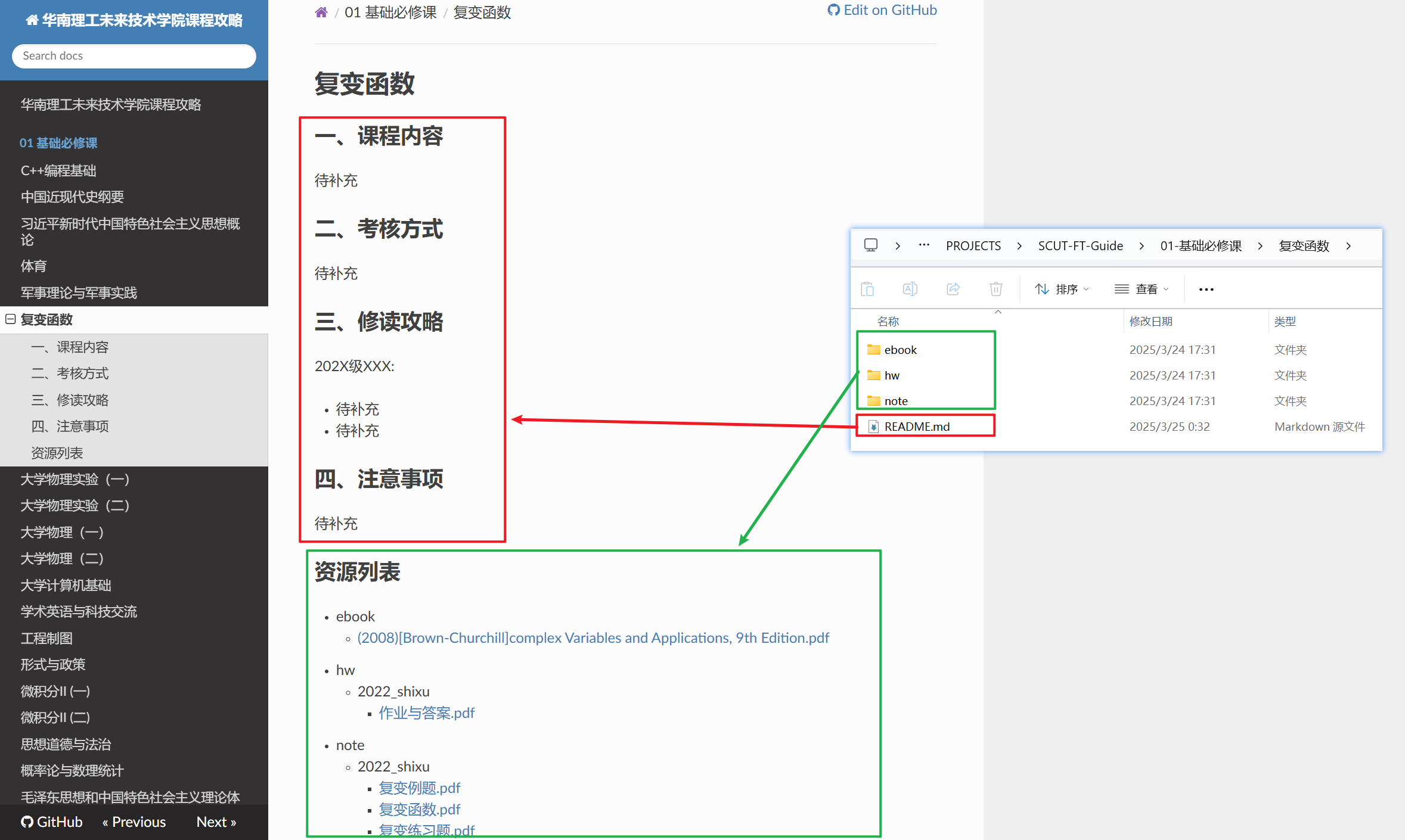
- 每个课程文件夹内存在一个
README.md文件,用于作为生成的对应课程页面的index.html内容的一部分,课程文件夹内的其他子文件夹统一视作资源文件,由脚本遍历生成资源文件列表置于index.html末尾 - 我们需要一个脚本来遍历所有课程组内的所有课程,为每个课程生成上述的
index.html文件,示例项目根目录下的update.py脚本如下,你可以根据不同的资料组织形式灵活修改脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
import os
from urllib.parse import quote
# 排除的目录列表,不包括在文件遍历中
EXCLUDE_DIRS = ['.git', 'docs', '.vscode']
# 需要特别处理的 README.md 文件
README_MD = ['README.md']
# 支持的文本文件扩展名,文本文件会生成文本链接
TXT_EXTS = ['md', 'txt']
# GitHub上文本文件的访问URL前缀
TXT_URL_PREFIX = 'https://github.com/OpenFuTech/SCUT-FT-Guide/blob/master/'
# GitHub上二进制文件的访问URL前缀
BIN_URL_PREFIX = 'https://github.com/OpenFuTech/SCUT-FT-Guide/raw/master/'
def GenerateFileList(courseGroup: str, course: str):
"""
遍历指定课程组和课程目录,生成文件列表的 Markdown 格式内容
"""
# 用于存储所有文件的Markdown格式内容
filelistTexts = '## 资源列表\n'
# 用于存储README.md文件的路径
readmePath = ''
# 遍历课程目录及其子目录
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(os.path.join(courseGroup, course)):
# 排序文件名
files.sort()
# 计算当前目录层级,根目录为1
level = root.replace(courseGroup, '').count(os.sep)
# 根据层级决定缩进量,根目录不个缩进,根目录下的文件夹0个缩进
indent = ' ' * 4 * (level - 2)
# 添加当前目录名到文件列表,跳过根目录
if (level > 1):
filelistTexts += '{}- {}\n'.format(indent, os.path.basename(root))
# 文件的缩进量(比目录多一级)
subindent = ' ' * 4 * (level - 1)
for f in files:
# 排除README.md文件
if f not in README_MD:
# 如果是md、txt等文本文件,生成GitHub页面链接
if f.split('.')[-1] in TXT_EXTS:
filelistTexts += '{}- [{}]({})\n'.format(subindent, f, TXT_URL_PREFIX + quote('{}/{}'.format(root, f)))
# 如果是其他文件(如二进制文件),生成raw内容链接
else:
filelistTexts += '{}- [{}]({})\n'.format(subindent, f, BIN_URL_PREFIX + quote('{}/{}'.format(root, f)))
# 如果是README.md文件,且该文件是课程根目录中的README.md
elif root == os.path.join(courseGroup, course) and readmePath == '':
# 保存README.md文件路径
readmePath = '{}/{}'.format(root, f)
return filelistTexts, readmePath
def GenerateMarkdown(courseGroup: str, course: str, filelistTexts: str, readmePath: str):
"""
生成并保存课程的Markdown文件,包含课程标题、README.md、文件资源列表
"""
# 组合最终的文本内容,先添加文件列表,然后如果有README.md,添加它
finalTexts = ['\n\n', filelistTexts]
if readmePath:
# 如果存在README.md,读取其内容
with open(readmePath, 'r') as file:
# 将README.md的内容添加到文件列表前
finalTexts = file.readlines() + finalTexts
# 将课程文件夹标题添加在开头
titleText = ['# {}\n\n'.format(course)]
finalTexts = titleText + finalTexts
# 将最终的内容写入到docs/{courseGroup}/{course}.md文件
os.makedirs(f'docs/{courseGroup}', exist_ok=True)
with open(f'docs/{courseGroup}/{course}.md', 'w') as file:
file.writelines(finalTexts)
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
1. 若docs目录不存在则创建
2. 遍历根目录中的所有课程组目录
3. 生成每个课程的Markdown文件
4. 将主README.md复制到docs/index.md
"""
# 如果docs目录不存在,创建它
if not os.path.isdir('docs'):
os.mkdir('docs')
# 遍历当前目录,筛选出所有有效的课程组目录(不包括排除目录EXCLUDE_DIRS)
courseGroups = list(filter(lambda x: os.path.isdir(x) and (
x not in EXCLUDE_DIRS), os.listdir('.')))
# 对每个课程组目录,生成文件列表并保存为Markdown文件
for courseGroup in courseGroups:
# 遍历课程组目录,筛选出所有有效的课程目录
courses = list(filter(lambda x: os.path.isdir(os.path.join(courseGroup, x)), os.listdir(courseGroup)))
for course in courses:
# 获取文件列表和README.md路径
filelistTexts, readmePath = GenerateFileList(courseGroup, course)
# 生成并保存课程的Markdown文件
GenerateMarkdown(courseGroup, course, filelistTexts, readmePath)
# 读取根目录下的README.md文件
with open('README.md', 'r') as file:
mainreadmeLines = file.readlines()
# 将根目录README.md的内容复制到docs/index.md
with open('docs/index.md', 'w') as file:
file.writelines(mainreadmeLines)
- 该脚本生成的内容形式示例如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
# 课程文件夹同名标题
粘贴README.md内的内容
## 资源列表
- ...
3.2.3 创建Actions工作流
- 然后我们需要在根目录下创建
.github文件夹,在该文件夹下创建workflows文件夹,其内创建一个.yml文件以配置Github Actions工作流,如下main.yml所示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# This is a basic workflow to help you get started with Actions
name: MkDocs
# Controls when the action will run. Triggers the workflow on push or pull request
# events but only for the main branch
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
permissions:
contents: write # 授予写入权限
# A workflow run is made up of one or more jobs that can run sequentially or in parallel
jobs:
# This workflow contains a single job called "build"
build:
# The type of runner that the job will run on
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# Steps represent a sequence of tasks that will be executed as part of the job
steps:
# Checks-out your repository under $GITHUB_WORKSPACE, so your job can access it
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: 3.x
- name: Install Dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Update Directory
run: python update.py
- name: Deploy Documents
uses: mhausenblas/mkdocs-deploy-gh-pages@nomaterial
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
- 该工作流每当远程仓库的分支
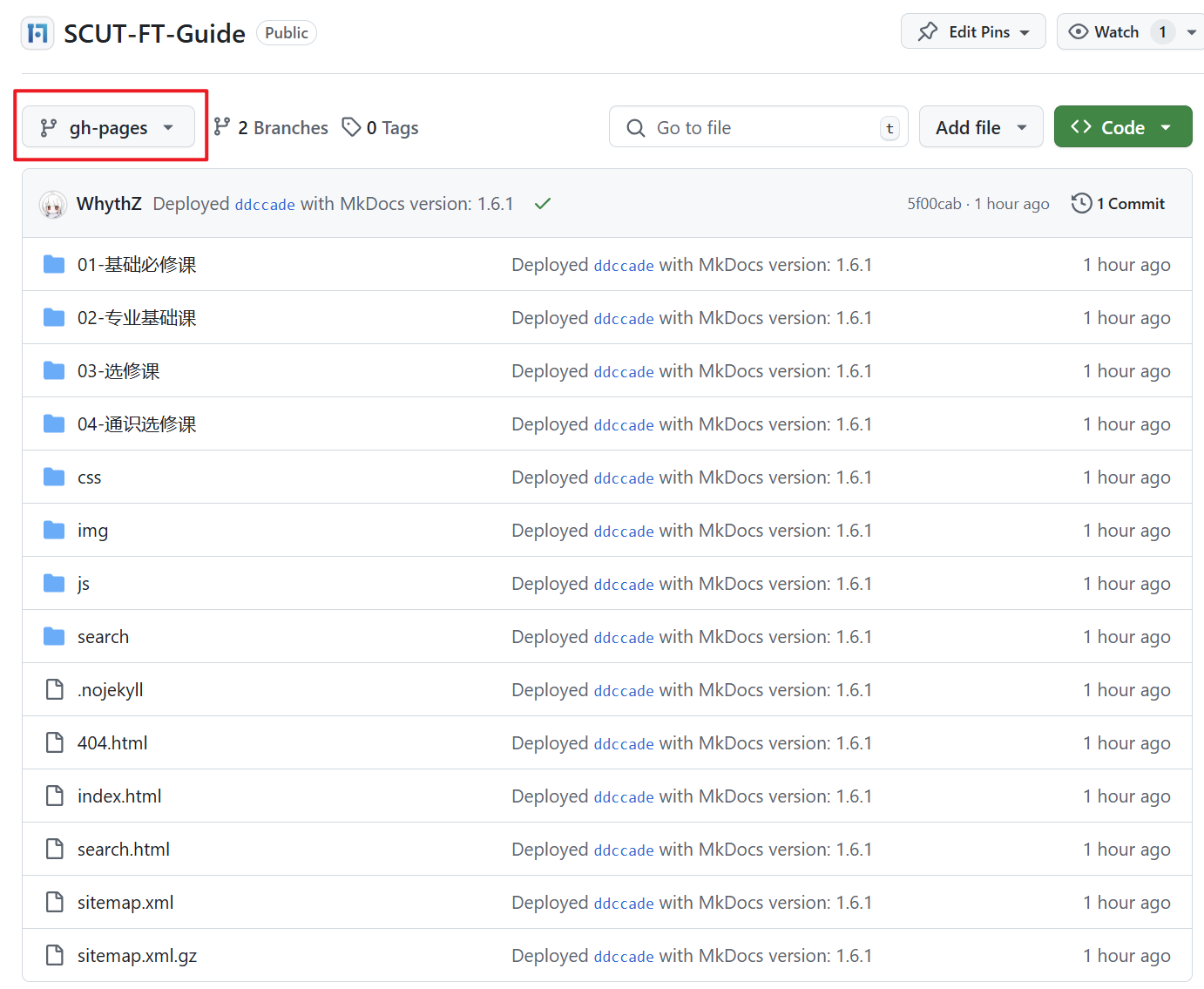
main发生新的提交时被触发,执行update.py脚本将页面内容生成至gh-pages分支 - 执行该工作流前必须创建一个名为
gh-pages的分支(然后最好将内容清空),并push到远程仓库以确保分支存在,否则工作流无法找到该分支
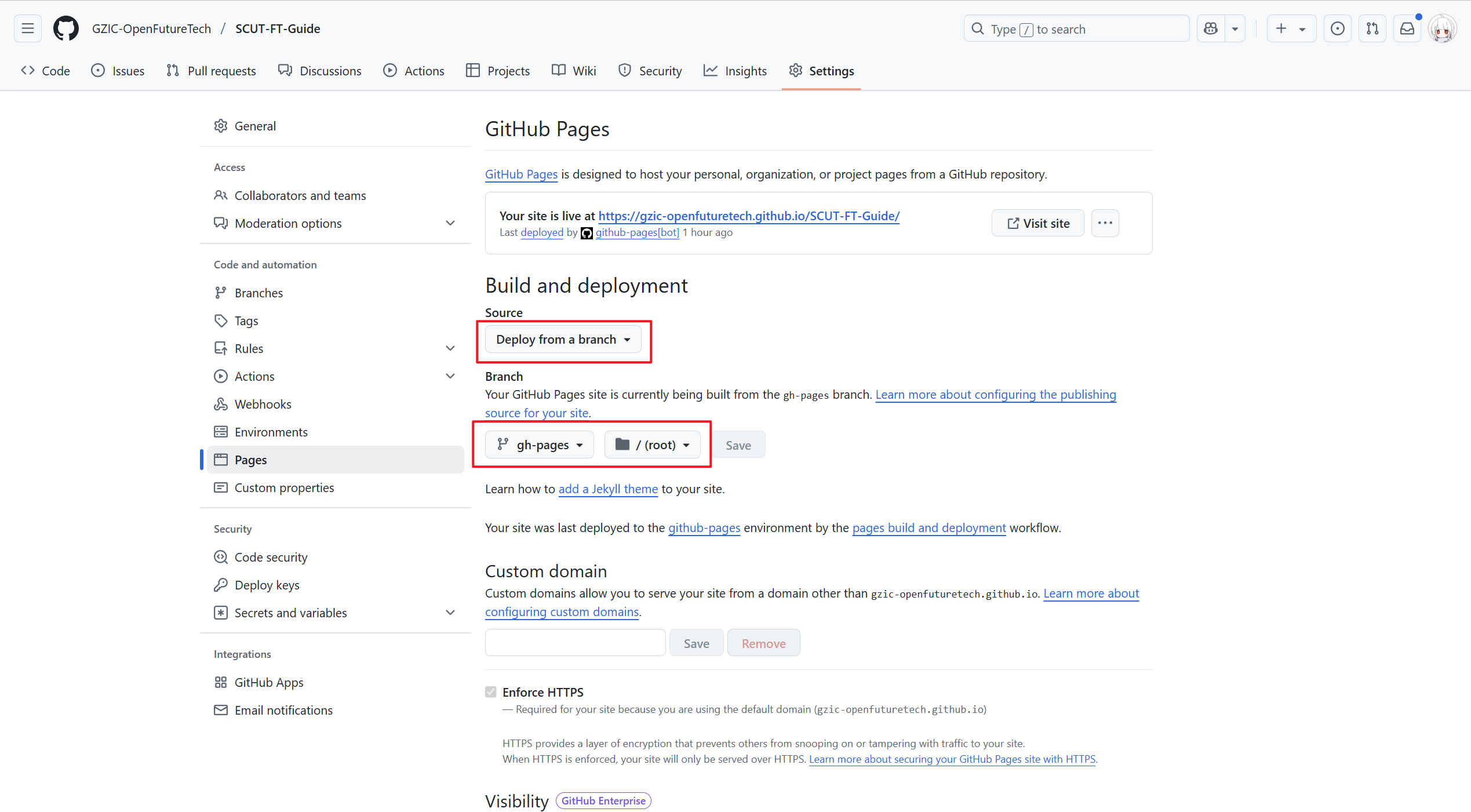
3.2.4 在Github发布Page
- 完成上述步骤后(均在
main分支进行),将更新push到main分支触发工作流,执行完毕后构建好的文件即存在于gh-pages分支下
- 然后使用该分支发布Github Pages即可得到页面
本文由作者按照 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 进行授权